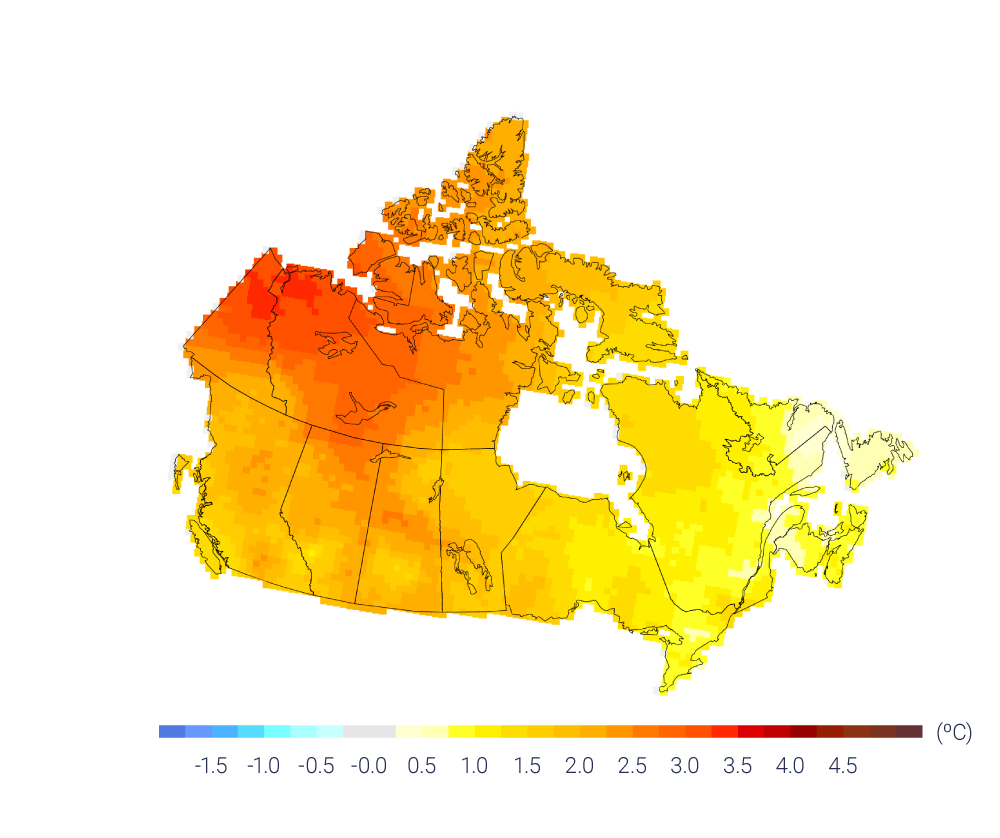
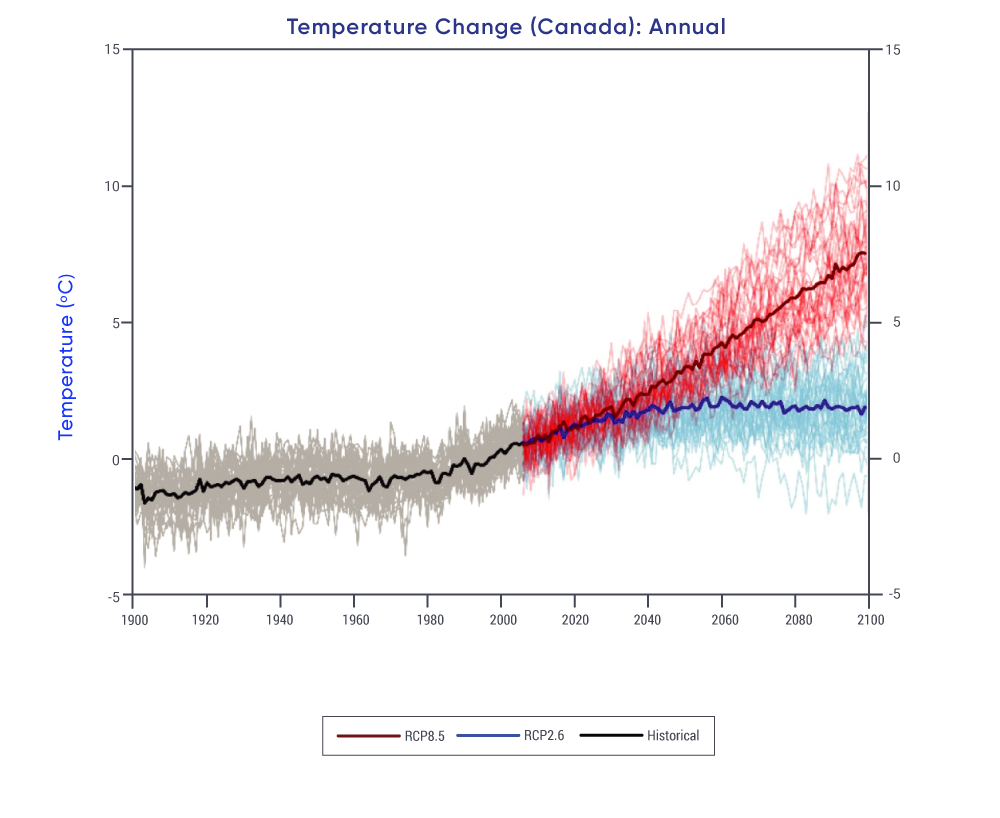
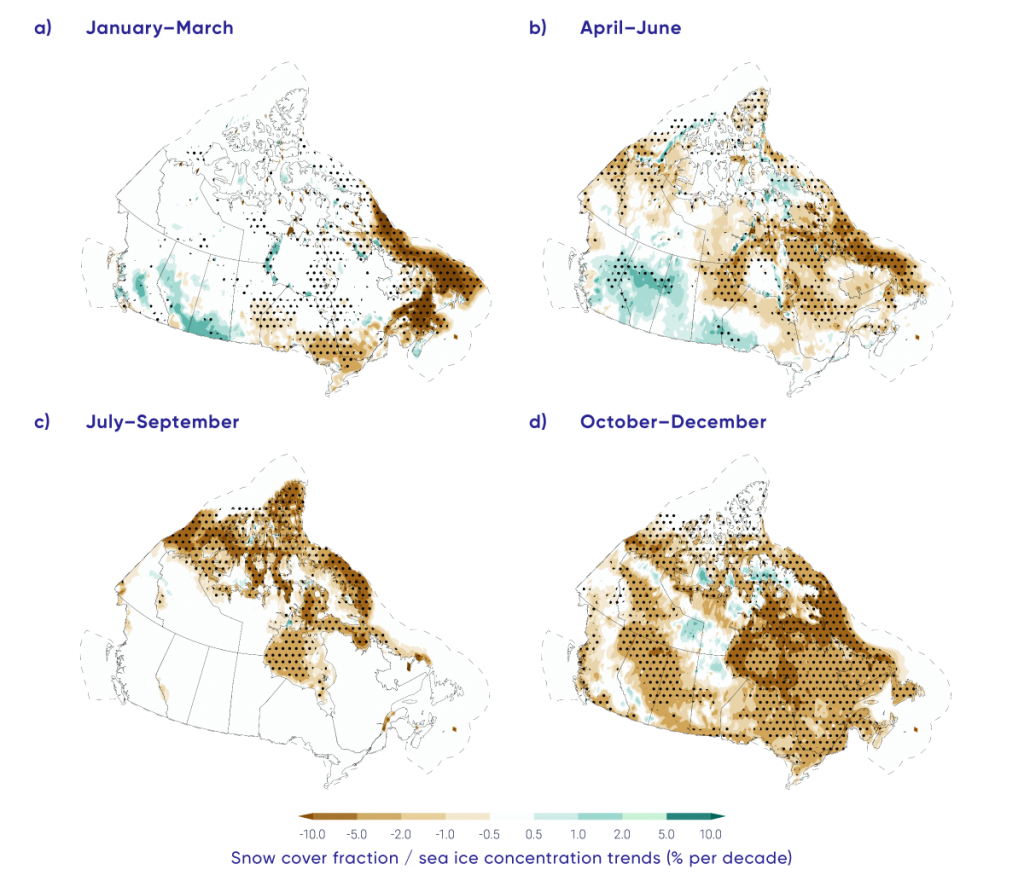
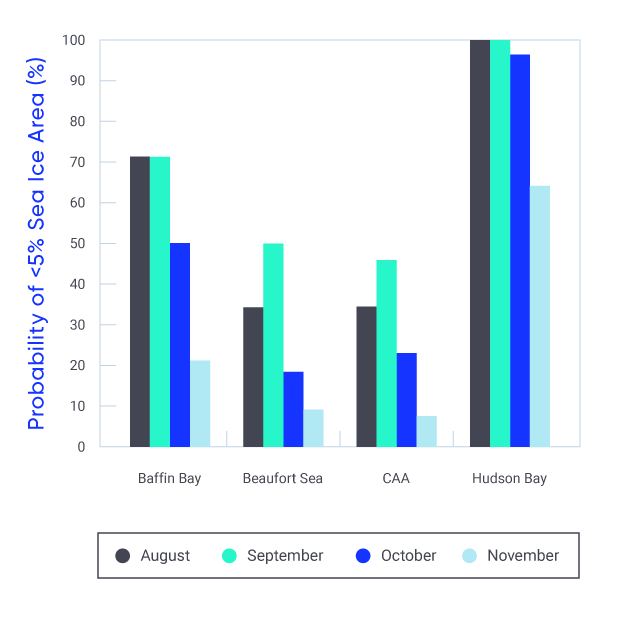
Temperature extremes have changed in Canada, consistent with the increase in mean temperature. Extreme warm temperatures have become hotter, while extreme cold temperatures have become less cold. {4.2}
Most of the observed increase in (warming of) the coldest and warmest daily temperatures in Canada (1948–2012) can be attributed to human influence. Warming has also led to an increased risk of extreme fire weather in parts of western Canada. {4.2, 4.3}
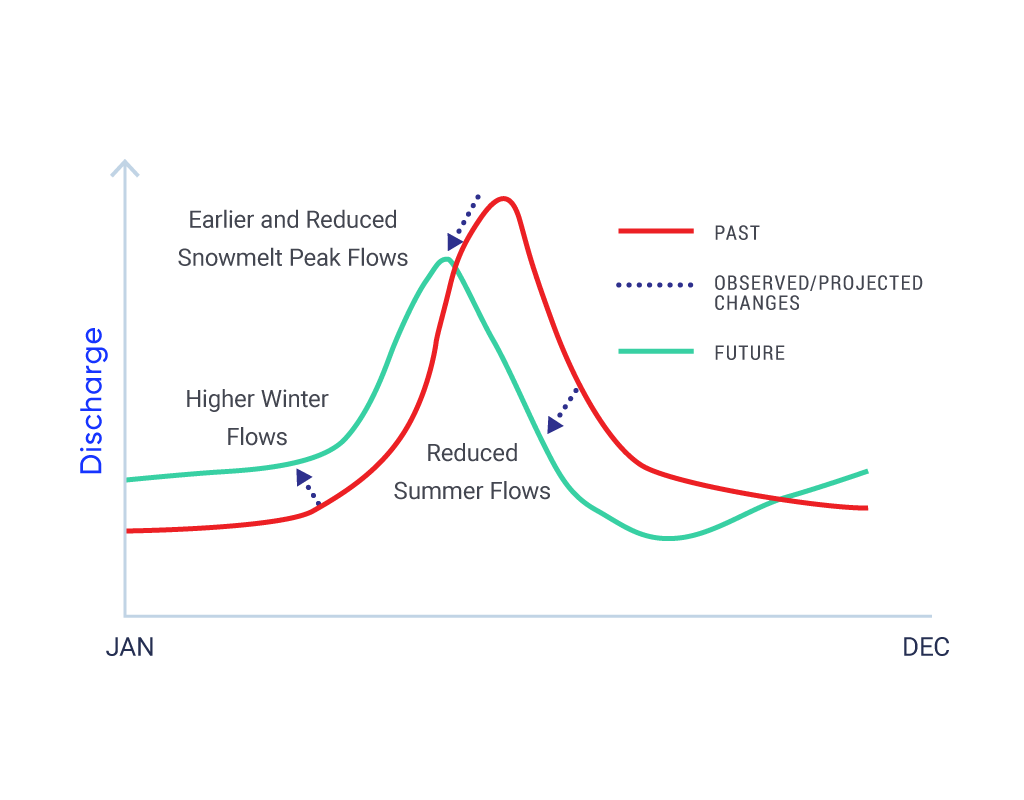
In the future, a warmer climate will intensify some weather extremes. Extreme hot temperatures will become more frequent and more intense. This will increase the severity of heatwaves, and contribute to increased drought and wildfire risks. While inland flooding results from multiple factors, more intense rainfalls will increase urban flood risks. It is uncertain how warmer temperatures and smaller snowpacks will combine to affect the frequency and magnitude of snowmelt-related flooding. {4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 5.2, 6.2}
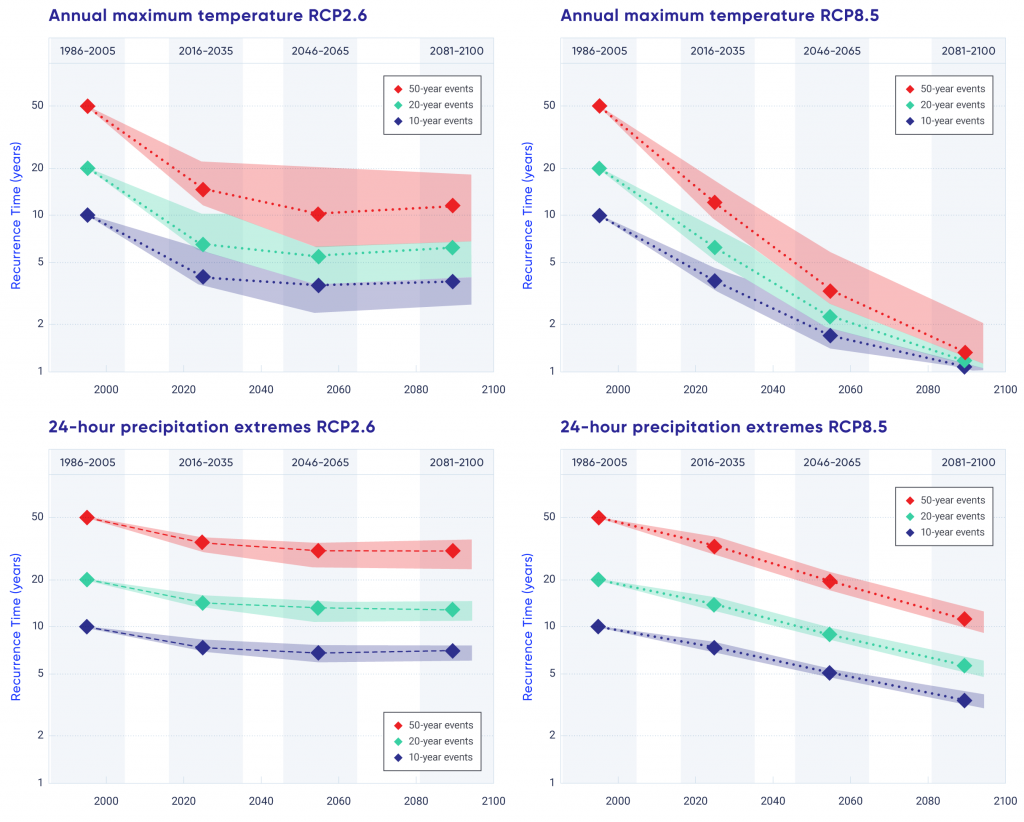
Changes in hot and cold extremes are projected to continue in the future, with the magnitude of the change proportional to the magnitude of the mean temperature change. For example, the annual highest daily temperature that currently occurs once every 20 years, on average, will become a once in 5-year event by mid-century under a low emission scenario (a four-fold increase in frequency) and a once in 2-year event by mid-century under a high emission scenario (a ten-fold increase in frequency). In the future, higher temperatures will contribute to an increased risk of extreme fire weather across much of Canada. {4.2, 4.3}
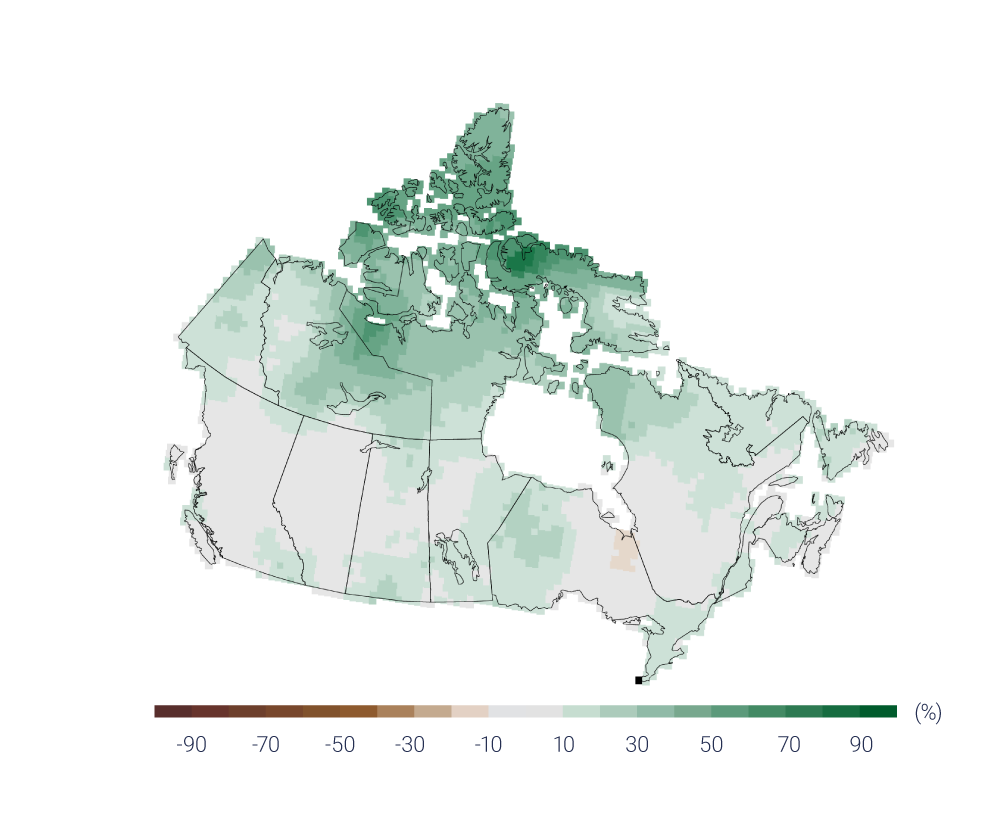
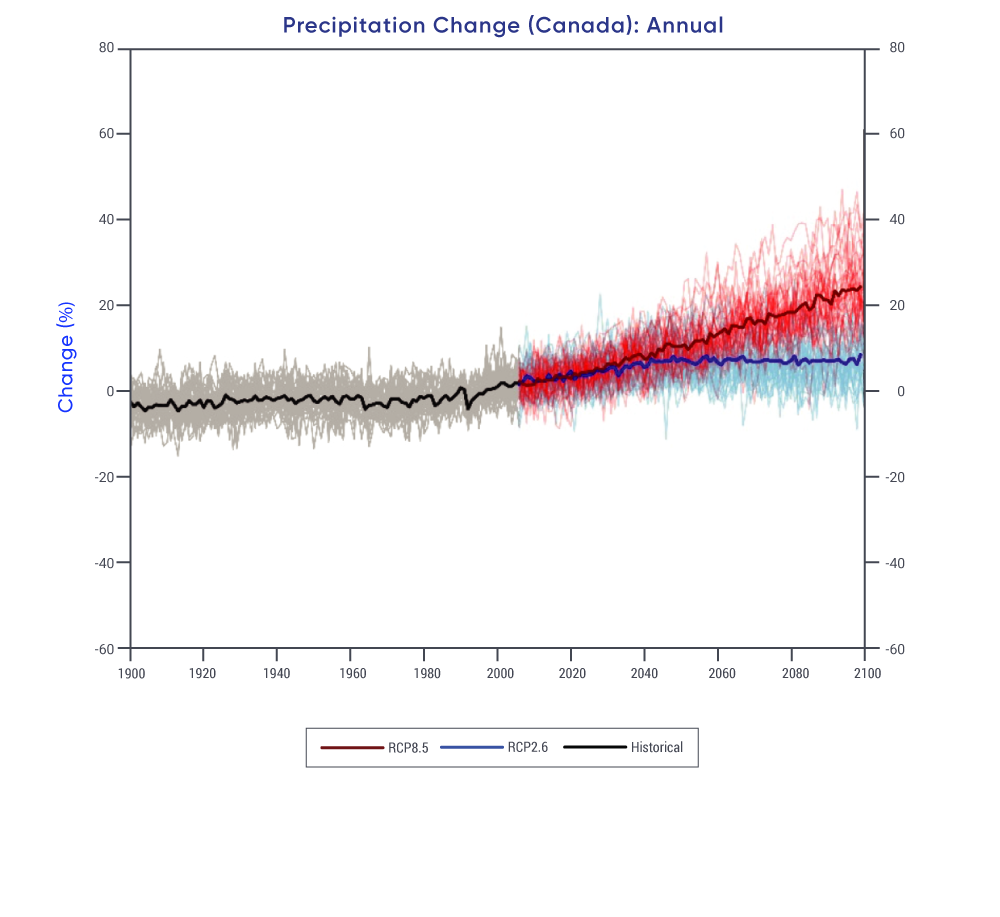
Extreme precipitation amounts accumulated over a day or shorter are projected to increase; thus, there is potential for a higher incidence of rain-generated local flooding, including in urban areas. {4.3, 6.2}
Future droughts and soil moisture deficits are projected with medium confidence to be more frequent and intense across the southern Canadian Prairies and interior British Columbia during summer at the end of the century under a high emission scenario. {6.4}